- Product Info
- SUMIKASUPER LCP
- Electrical properties of LCP
Electrical properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
Volume resistivity
The volume resistivity of a material is defined as the electrical resistance of a unit cube of that material, and is measured by the current that flows through the material when a voltage of DC 500V is applied to the material for one minute. The higher the electrical insulation, the higher the volume resistivity. SUMIKASUPER LCP has high insulation due to the strong orientation of the skin layer.
Figure 3-6-1 Volume resistivity and dielectric breakdown voltage of SUMIKASUPER LCP
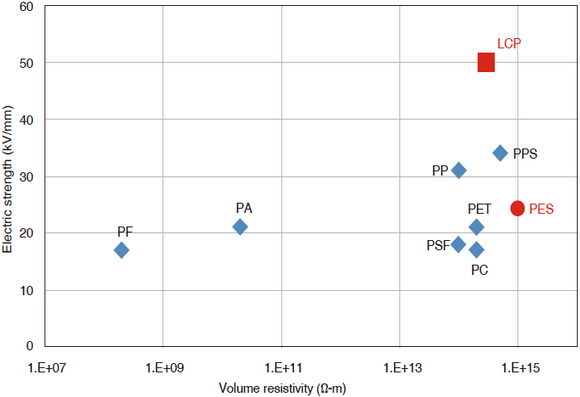
Insulation properties
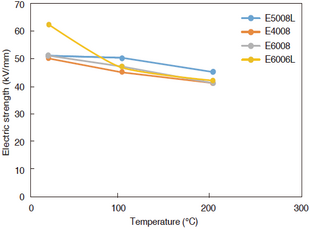
Breakdown voltage is an index that indicates how high a voltage a material can withstand without dielectric breakdown. Test results are reported in kV/mm, but the breakdown voltage is also affected by the thickness and temperature of the test piece. As with tensile strength, the thinner the material is, the higher the breakdown voltage of SUMIKASUPER LCP is. In addition, the breakdown voltage does not decrease easily even at high temperatures, and the material has excellent insulating properties.
Figure 3-6-2 Dependence of dielectric breakdown voltage on thickness of SUMIKASUPER LCP
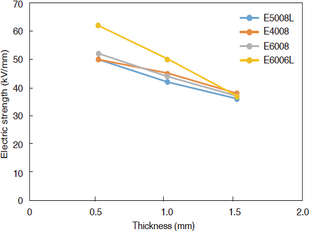
Figure 3-6-3 Temperature dependence of dielectric breakdown voltage of SUMIKASUPER LCP
Dielectric properties
The temperature and frequency dependence of the dielectric constant and dielectric tangent of SUMIKASUPER LCP is small and stable. In particular, LCP has a small dielectric tangent in the gigahertz range.
Figure 3-6-4 Temperature dependence of dielectric tangent
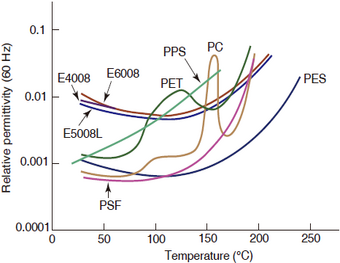
Figure 3-6-5 Frequency dependence of dielectric tangent

Table 3-6-1 Electrical properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
| Measurement items | Test method | E5008L | E5008 | E5204LB | E4008 | E4205R | E6008 | E6006L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dielectric constant | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | 4.7 | 4.7 | - | 4.5 | - | 4.4 | 4.3 |
| 1MHz | 4.2 | 4.2 | 3.1 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 3.7 | ||
| 1GHz | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 3.7 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 3.5 | |
| Dielectric tangent | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | 0.013 | 0.015 | - | 0.018 | - | 0.022 | 0.023 |
| 1MHz | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.018 | 0.034 | 0.013 | 0.032 | 0.034 | ||
| 1GHz | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.005 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.005 | |
| Measurement items | Test method | E6007LHF | E6807LHF | SR1009 | E6205L | SR1205L | E6808LHF | E6808UHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dielectric constant | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | - | 4.3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1MHz | 3.8 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | ||
| 1GHz | 3.8 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 3.6 | 3.5 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 3.6 | - | 4.0 | 2.8 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 3.6 | |
| Dielectric tangent | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | - | 0.020 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1MHz | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.007 | 0.038 | 0.033 | ||
| 1GHz | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 0.005 | - | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.004 | |
| Measurement items | Test method | SV6808THF | SV6808GHF | SR2506 | SR2507 | SZ6505HF | SZ6506HF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dielectric constant | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1MHz | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.5 | ||
| 1GHz | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.5 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 3.6 | |
| Dielectric tangent | 1kHz | IEC 60250 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1MHz | 0.012 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.023 | 0.011 | ||
| 1GHz | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.005 | ||
| 10GHz | IEC 62810 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | |
