- Product Info
- SUMIKASUPER LCP
- Other properties of LCP
Other properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
Vibration damping properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
SUMIKASUPER LCP has high rigidity and vibration damping properties, and therefore has superior vibration damping properties compared to other resins. The relationship between loss factor and flexural modulus is shown in Figure 3-7-1, and it shows a high loss factor while having a high modulus of elasticity.
Figure 3-7-1 Relationship between loss factor and flexural modulus of SUMIKASUPER LCP
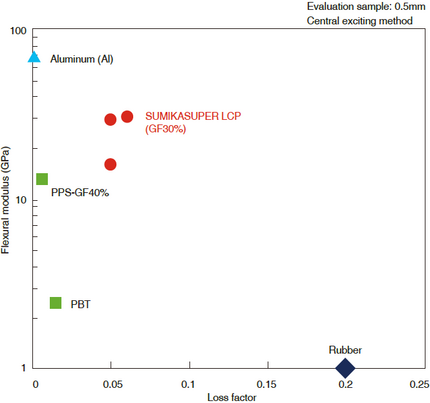
Figure 3-7-2 Comparison of vibration damping properties between LCP and PPS
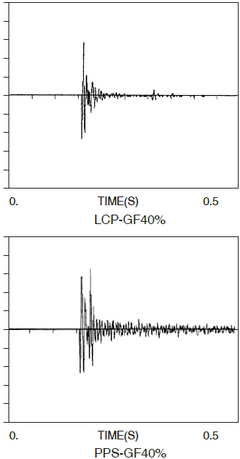
Figure 3-7-3 Resonance characteristics of SUMIKASUPER LCP
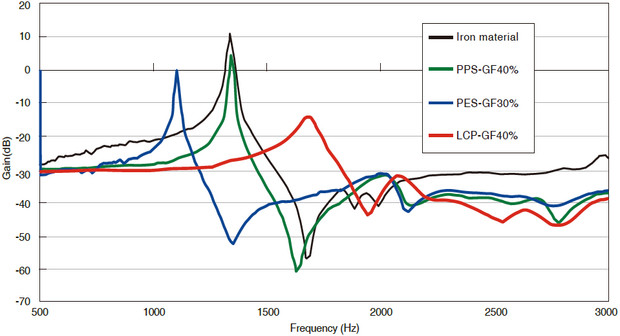
Table 3-7-1 Comparison of SUMIKASUPER LCP with other resins
| Resonant frequency (Hz) | Loss factor | |
|---|---|---|
| LCP-GF40% | 1,680 | 0.0491 |
| PES-GF30% | 1,100 | 0.0092 |
| PPS-GF40% | 1,340 | 0.0093 |
| Iron | 1,340 | 0.0095 |
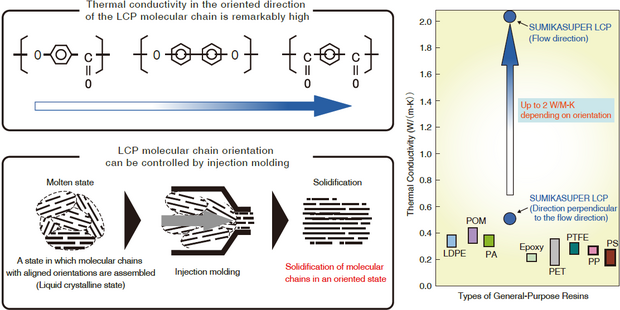
Thermal conductivity of SUMIKASUPER LCP
The thermal conductivity of SUMIKASUPER LCP changes depending on the orientation of the resin, and it shows high thermal conductivity in the flow direction. In addition, compared to the thermal conductivity of LCP resin, the thermal conductivity of fillers such as glass fiber is higher, so the thermal conductivity varies depending on the type and content of fillers.
Figure 3-7-4 Thermal conductivity of SUMIKASUPER LCP
Gas barrier properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
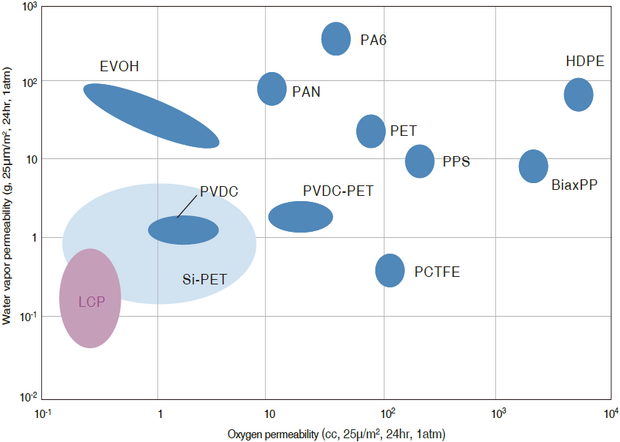
Gas barrier properties are the amount of gas that permeates 1m2 in 24 hours, called the permeation rate. The slower the permeation rate, the less the amount of gas that permeates, and the better the barrier properties. Normally, gas barrier properties are inversely proportional to the thickness of the test piece, so the thickness in the figure below is a unified value of 25μm (cc・25μm/m2 ・24hr・1atm). SUMIKASUPER LCP has low permeation rates for both water vapor and oxygen permeability, and has excellent gas barrier properties.
Figure 3-7-5 Gas barrier properties of SUMIKASUPER LCP
CAE analysis of SUMIKASUPER LCP
CAE (computer-aided engineering) analysis allows you to evaluate (simulate) design problems in a product that has been artificially reproduced on a computer. Some of the technical data required for CAE is shown in the table below. The data below is data measured for CAE analysis. If you have technical data required for CAE analysis, please contact us.
Table 3-7-2 CAE characteristics of SUMIKASUPER LCP 1
| Test method | unit | E5204L | E5006L | E4008 | E6006L | E6008 | E6807T | E6007LHF | E6808LHF | E6810LHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific heat | ASTM E1269 | J/(kg K) | 1,067 | 1,068 | 812 | 839 | 812 | 1,012 | 967 | 1,009 | 974 |
| Thermal Conductivity | ISO 22007-2 | W/(m K) | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.70 |
| Melt Density | PVT method | g/cm3 | 1.10 | 1.35 | 1.54 | 1.42 | 1.54 | 1.52 | 1.50 | 1.53 | 1.65 |
| Solid Density | PVT method | g/cm3 | 1.23 | 1.58 | 1.70 | 1.59 | 1.70 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 1.73 | 1.84 |
| Young's Modulus (MD) | ASTM D638 | MPa | 8,000 | - | 13,000 | 14,000 | 13,000 | 8,700 | 14,000 | 11,000 | 9,900 |
| Young's Modulus (TD) | ASTM D638 | MPa | 3,000 | - | 3,600 | 3,800 | 3,600 | 3,900 | 5,100 | 4,800 | 5,600 |
| Poisson's ratio (MD) | ASTM D638 | - | 0.43 | - | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.28 |
| Poisson's ratio (TD) | ASTM D638 | - | 0.86 | - | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.73 |
Table 3-7-3 CAE characteristics of SUMIKASUPER LCP 2
| Test method | unit | E6808UHF | SV6808THF | SV6808GHF | SZ6505HF | SZ6506HF | SR2506 | SR2507 | SR1009L | SR1205L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific heat | ASTM E1269 | J/(kg K) | 1,203 | 920 | 890 | 1,121 | 1,110 | 1,042 | 979 | 897 | 856 |
| Thermal Conductivity | ISO 22007-2 | W/(m K) | 0.33 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.29 | 0.38 |
| Melt Density | PVT method | g/cm3 | 1.54 | 1.57 | 1.53 | 1.42 | 1.44 | 1.46 | 1.54 | 1.60 | 1.06 |
| Solid Density | PVT method | g/cm3 | 1.73 | 1.73 | 1.69 | 1.58 | 1.63 | 1.64 | 1.69 | 1.75 | 1.16 |
| Young's Modulus (MD) | ASTM D638 | MPa | 8,000 | 8,000 | 10,000 | 11,200 | 11,000 | 12,000 | 13,000 | 14,000 | 7,600 |
| Young's Modulus (TD) | ASTM D638 | MPa | 4,100 | 4,600 | 4,800 | 5,900 | 6,300 | 6,000 | 8,100 | 5,800 | 4,200 |
| Poisson's ratio (MD) | ASTM D638 | - | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.40 |
| Poisson's ratio (TD) | ASTM D638 | - | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.64 | 0.53 |
